What Are The 6 Types Of Society: A Comprehensive Exploration
Different Types Of Societies
Keywords searched by users: What are the 6 types of society Kind of society, Element of society, 5 types of society, Industrial society, Function of society, What society includes, Culture and society, types of societies and its characteristics
What Is The 6 Society?
Understanding the Six Types of Society in Sociology
Author: Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch)
Peer Reviewed by: Chris Drew (PhD)
Published Date: August 26, 2023
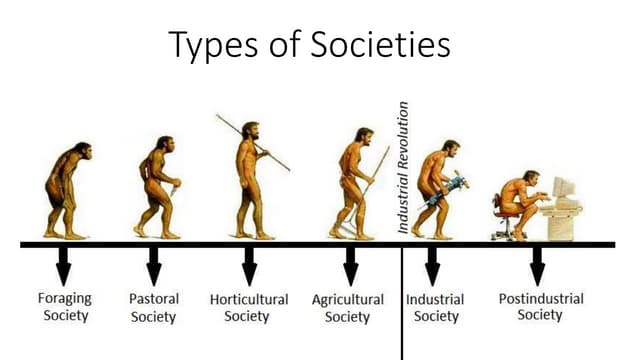
In the field of sociology, the concept of the “Six Society Types” serves as a foundational framework for categorizing human societies throughout history. This framework, originally proposed by renowned sociologists, encompasses six distinct categories: hunter-gatherer, pastoral, horticultural, agricultural, industrial, and post-industrial societies. These categories represent crucial milestones in the evolution of human civilization, marking significant shifts in how societies organized and sustained themselves over time. To provide a more comprehensive understanding of this topic, let’s delve into the defining characteristics and key features of each society type.
While the original publication date of this information is not provided, it’s worth noting that this framework remains a fundamental element of sociological study as of August 26, 2023. This enduring relevance underscores the importance of comprehending the nuances of each society type and their contributions to the broader narrative of human history.
What Are The Six 6 Types Of Societies And Their Meaning?
Throughout history, societies have evolved through distinct stages, each with its own unique characteristics and implications. These six fundamental types of societies are: hunting-and-gathering, horticultural, pastoral, agricultural, industrial, and postindustrial.
-
Hunting-and-Gathering Societies: These were the earliest human societies, primarily characterized by a nomadic lifestyle of hunting animals and gathering plants for sustenance. In these societies, gender roles were typically more equal due to the shared responsibilities of gathering and hunting.
-
Horticultural Societies: Transitioning from a nomadic lifestyle, horticultural societies emerged as people began to cultivate plants for food. This shift allowed for more settled communities and the development of basic agricultural practices.
-
Pastoral Societies: In pastoral societies, people primarily relied on the domestication of animals for their livelihoods. These societies were often semi-nomadic, moving their herds to find fresh grazing land.
-
Agricultural Societies: The advent of agriculture marked a significant turning point in human history. Agricultural societies were characterized by the widespread cultivation of crops and the establishment of permanent settlements. This shift led to surpluses of food, enabling population growth and the emergence of social hierarchies.
-
Industrial Societies: The Industrial Revolution brought about a dramatic transformation in society. Industrial societies were defined by mechanized production, urbanization, and a shift from agrarian economies to manufacturing and industry. This era saw significant wealth and power disparities, as well as increased competition among nations.
-
Postindustrial Societies: As we progressed into the modern age, postindustrial societies emerged. These are characterized by a heavy reliance on technology, information, and services. Postindustrial societies often prioritize knowledge-based economies, leading to a different set of social and economic challenges.
As societies advanced from hunting-and-gathering to postindustrial stages, they experienced shifts in gender roles, wealth distribution, and their interactions with other societies. These transitions were often accompanied by increased inequality, competitiveness, and, at times, conflict with neighboring societies. Understanding these societal stages provides valuable insights into the complexities of human development and organization across history.
What Are The 10 Characteristics Of Society?
What are the 10 characteristics of a society? A society possesses a set of defining traits that shape its structure and functioning. These characteristics encompass both the commonalities and distinctions among its members, promoting interconnectedness and influencing the dynamics within the community or group. These fundamental characteristics include:
-
Likeness: This denotes the existence of shared traits or attributes among members within a society, fostering a sense of unity based on mutual aspects.
-
Reciprocal Awareness: Members within a society are generally aware of each other’s existence and roles, which contributes to the cohesion and functioning of the group.
-
Differences: While societies exhibit similarities, they also embrace diversity, with individuals possessing unique qualities and attributes that contribute to the richness of the community.
-
Interdependence: Societies rely on interconnections and mutual reliance among their members, which ensures the fulfillment of various needs and roles within the group.
-
Cooperation: Collaboration and joint efforts are essential in societies, as they enable individuals to work together for common goals, thereby strengthening the community.
-
Conflict: Contrary to harmony, conflicts may arise within societies due to differences in perspectives, interests, or goals. The management of these conflicts is crucial for the group’s stability and growth.
These six characteristics provide a foundational understanding of societal dynamics, but it’s important to note that there are four additional characteristics that can further elucidate the complexities of societies.
Found 21 What are the 6 types of society




Categories: Discover 48 What Are The 6 Types Of Society
See more here: khodatnenbinhchau.com

By Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) and Peer Reviewed by Chris Drew (PhD) / August 26, 2023. The six types of society in sociology are hunter-gatherer, pastoral, horticultural, agricultural, industrial, and post-industrial.The major types of societies historically have been hunting-and-gathering, horticultural, pastoral, agricultural, industrial, and postindustrial. As societies developed and grew larger, they became more unequal in terms of gender and wealth and also more competitive and even warlike with other societies.
- Hunting and gathering societies.
- Pastoral societies.
- Horticultural societies.
- Agricultural societies.
- Industrial societies.
- Post-industrial societies.
- Likeness- This refers to similar traits amongst members in a community or group on the basis of mutual aspects.
- Reciprocal awareness.
- Differences.
- Interdependence.
- Cooperation.
- Conflict.
- Likeness: Likeness of members in a social group is the primary basis of their mutuality. …
- The Reciprocal Awareness: Likeness is generative of reciprocity. …
- Differences: …
- Interdependence: …
- Cooperation: …
- Conflict:
Learn more about the topic What are the 6 types of society.
- Society: Types, Characteristics & Examples – Study.com
- 6 Types of Societies (With 21 Examples) (2023)
- 5.2 The Development of Modern Society – Sociology
- To Understand the Most Important Characteristics of a Society,: IELTS …
- 6 Basic Elements or Characteristics which Constitutes Society (927 …
- 5.1 Social Structure: The Building Blocks of Social Life – Sociology
See more: khodatnenbinhchau.com/category/food